
StudySmarter - The all-in-one study app.
4.8 • +11k Ratings
More than 3 Million Downloads
Free
Americas
Europe
Malaria, Tuberculosis, COVID-19, and the common cold are all examples of diseases that are caused by pathogens which can be transmitted from one person to another. Each disease can be spread in different ways and thus requires different safety measures or precautions to avoid transmission: covering our mouths when we cough or cooking food properly are examples of prevention measures we can each take to prevent the spread of communicable diseases!



Lerne mit deinen Freunden und bleibe auf dem richtigen Kurs mit deinen persönlichen Lernstatistiken
Jetzt kostenlos anmeldenMalaria, Tuberculosis, COVID-19, and the common cold are all examples of diseases that are caused by pathogens which can be transmitted from one person to another. Each disease can be spread in different ways and thus requires different safety measures or precautions to avoid transmission: covering our mouths when we cough or cooking food properly are examples of prevention measures we can each take to prevent the spread of communicable diseases!
Communicable diseases, also known as infectious diseases, are illnesses caused by Microorganisms called pathogens that can spread between organisms and infect people, Animals or Plants simply through exposure to the pathogen or other infected organism.
These diseases can pass on from one person to another in many different ways, depending on how the pathogen propagates. It's even possible for the pathogen to be transmitted between different species.
For example, dogs can transmit the rabies pathogen to people via dog bites, and cows can pass on the TB pathogenic microorganism via their milk products.
Communicable diseases can be caused directly by a pathogen or through toxins that that pathogen produces.
COVID-19 is a great example of a communicable disease. COVID-19 is a disease caused by a viral pathogen that can be spread from person to person via airborne droplets. These droplets can be released and spread to others when a person speaks, coughs, breathes or sneezes.
The reason behind wearing masks was that they helped to prevent the spread of these airborne droplets by covering our mouths and nose.
COVID-19 vaccinations were also helpful in combatting the virus. These vaccinations help prepare our body if it ever comes into contact with COVID-19's viral agent.
The opposite of communicable diseases is non-communicable diseases like heart disease. These diseases can't pass from one person to another via a pathogen!
Read more about them in our article on Non-Communicable Diseases!
Communicable diseases can be classified depending on the agent that causes them, i.e. the responsible pathogen. Each pathogen has a different way of transmission, a different time that it can survive without a host, and different virulence (harm potential).
Pathogens are Microorganisms that have the potential to cause harm/disease. These can infect and cause illness in various organisms, including humans, Animals and Plants.
Pathogens can affect both Animal and Plant Cells. We will look at examples of each. The pathogen's effect on the host will depend on the host and the pathogen itself.
We will discuss four main types of pathogens: Bacteria, Viruses, Fungi, and Protists.
Each pathogen may exert its effect and cause disease by different methods.
Viruses can lysate (burst) Cells while exiting from them,
and Bacteria can produce toxins that kill or block the function of the patient's Cells.
Understanding their methods to cause disease or pathophysiology is key to understanding how to treat the conditions they cause. Equally important is to know how they propagate and transmit their disease between different organisms. Pathogens can spread in many ways, so understanding this is important to develop measures that break the transmission chain.
Some of the most common ways that different pathogens can be transmitted include:
Vectors and fomites
Airborne (through the air)
Contaminated food and water
Direct contact with an infected person
Communicable diseases can also be transmitted through bodily fluids like Blood, saliva or semen. This is an important subtype of communicable disease known as sexually transmitted infections/diseases (STI/STDs).
Gonorrhoea, for example, is an STI. A mechanical barrier such as condoms should be used during sexual intercourse to avoid the transmission of STIs.
A vector is an organism that carries the pathogen without presenting symptoms. An example of this is how the Plasmodium protist (pathogen) is transported by mosquitos (vector), causing Malaria in humans.
A fomite is equivalent to an inert vector (for example, clothes with the sweat or saliva of an infected person).
Depending on how the pathogen is spread, there are different methods that we can use to stop their transmission:
Cleaning surfaces.
Ensuring food is correctly cooked.
Using mosquito nets and repellent (in the case of malaria).
Cover our noses and mouths when sneezing or coughing.
Make sure water is safe to drink and boil when necessary.
Communicable diseases can cause serious harm to people, especially the more vulnerable members of society.
These include pregnant women, older people, newborn babies and those who already have weakened immune systems.
Due to the danger that these diseases can present to us, especially to the groups mentioned above, it's important that we control communicable diseases as much as possible. There are 3 different ways we can approach this; vaccination, preventing the spread of pathogens and treatments.
Vaccinations are fundamental aspects of modern healthcare. Vaccinations, in a nutshell, involve giving a weakened or modified version of a pathogen to a patient so that their body can mount an Immune Response without them showing symptoms or getting sick. This allows their body to create memory cells as part of the Immune Response. These memory cells can then remember the pathogen and the immune response required to destroy it. In this way, if the pathogen were to invade the body again, the Immune System could quickly and effectively deal with the pathogen, meaning the person will not get sick or show many symptoms.
The first immune response that our body produces against a specific antigen is called the primary immune response. The secondary immune response is the second time your body comes into contact with it. The secondary immune response is faster and more effective than the primary, hence why we get the primary response out of the way by vaccinating people!
Read all about it in our article Vaccinations.
Aside from vaccinations, we can also use various methods to prevent the spread of a pathogen in the community. If we think back to COVID-19, we all had to take some precautionary measures to prevent the spread of the COVID-19 Virus. These included social distancing, having social bubbles and wearing face masks, amongst other precautions. The type of measures we take to prevent the spread of a pathogen will depend on the route of transmission for the pathogen. Let's check some examples of different transmission routes of specific pathogens and how we can deal with them.
Pathogen | Disease | Route of transmission | How to prevent the spread |
Bacteria | Salmonella | Contaminated food | Thoroughly cook food and only cook on clean surfaces |
Virus | Flu | Airborne droplets | Flu jab, and cover nose when sneezing |
Protist | Malaria | Mosquitoes | Mosquito repellent, wear long clothes |
Athlete's foot | contact with infected skin scales | Wear appropriate footwear in public showers |
If all else fails, we have to resort to treatments once the pathogen has already infected the person. This is not ideal, however, modern medicine now means that many of these medications can treat patients back to full health a lot of the time. There are three main types of medications that we need to know about:
Antibiotics, which treat bacterial infections
Antifungal medications, which treat fungal infections
Antiviral drugs which treat viral infections
The importance of taking these medications only when necessary and for the correct length of time can not be overstated. Antibiotic resistance is likely to be one of society's greatest threats in the coming years. Antibiotic resistance describes the situation where Antibiotics that once worked against bacteria no longer have an effect. Some studies suggest that it now takes over 50 years to develop a new antibiotic, and only 3 years or even less for bacteria to develop resistance to that new antibiotic. At this rate, it won't be long until we have no antibiotics. Even worse, it won't be long until we have more superbugs, which are nearly impossible to treat and can cause havoc amongst hospital wards and even the general population!
Check out the article Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria.
As mentioned before, communicable diseases are divided into types of causative pathogens. There are four main types of pathogens: Viruses, Bacteria, Protists and Fungi. Below we take a look at each of the microorganisms and some examples of diseases they cause.
Viruses are very different from animal, plant, fungal and bacterial cells. Viral particles are much smaller than all of these cells and cannot even be seen with most Microscopes. Viruses are technically not living organisms, as they can only carry out their life cycle and reproduce once they invade host cells. In other words, they are obligate parasites as they don't have the machinery necessary to survive and reproduce on their own.
A virus's "life" cycle differs a lot from other pathogens. Viruses do not reproduce and replicate the same way as other pathogens. Instead, they replicate their DNA once they invade another cell. Once a viral particle has replicated inside a cell, it can then burst the host cell or bud away from it to leave and reach another cell to carry out the same process again.
Viruses have very strange life cycles and must invade other host cells to carry out most of their metabolic processes. The interesting thing about viruses is that they do not discriminate against cells when the time comes to pick one to invade! Viruses can invade animal cells, plant cells and even bacteria.
An example of a virus that invades bacteria is the bacteriophage virus. The word bacteriophage literally means bacteria eater!
One example of a viral disease affecting animal cells is HIV/AIDS. AIDS is a chronic (long-term) disease that is potentially life-threatening and is caused by the HIV pathogen. HIV is transmitted through sexual contact and contact with bodily fluids. It takes months after HIV infection before AIDS develops. AIDS is an immune condition, which means that it attacks the body's Immune System.
AIDS = Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome
HIV = Human Immunodeficiency Virus
The main viral infection you need to know about regarding plants is the tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) infection. As the name suggests, this virus infects tobacco and other plants. This virus affects the chloroplasts of Plant Leaves. The tobacco mosaic virus is transmitted by contact between plants.
Remember, chloroplasts are the organelle responsible for Photosynthesis! Read more about this vital reaction in the Photosynthesis article!
The leaves get a mosaic pattern and discolour when affected by the virus. Photosynthesis can no longer occur, so the plant cannot grow. This has an important economic impact on farmers. The tobacco mosaic virus cannot be cured, so farmers try to contain it within a certain area to prevent it from affecting more crops.
Learn more about TMV and HIV in our Viral Diseases article!
Bacterial Diseases are, as the name suggests, diseases caused by bacteria. It includes various diseases, from Tetanus to the Bubonic Plague. Some Bacterial Diseases' symptoms aren't caused by the bacteria themselves but by the toxins they release, such as Anthrax.
Bacteria are a type of prokaryotic organism. This means they do not have a nucleus and are smaller and less complex than other eukaryotic organisms like animal, plant and fungal cells.
Prokaryotic organisms have their genetic material free in the cytoplasm or found in plasmids, circular loops of DNA. Similarly to viruses, bacteria can reproduce rapidly within the human body.
Remember the differences between the two main types of cells? Read more about this in our article Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes!
Even though we are discussing bacteria in the context of pathogens, we must recognise that not all bacteria are pathogenic. Lots of bacteria live in our bodies, and we depend on them for functions like digestion. These Types of Bacteria are called commensal bacteria.
Bacteria are very different to viruses. Check out the Bacterial Diseases article to learn more about what diseases bacteria can cause!
Fungi are eukaryotic organisms, which means that they contain a nucleus.
Like bacteria, not all fungi cause diseases. For example, some yeasts (unicellular fungi) are very important and are used to make food, like bread.
A pathogenic fungus in animals is responsible for Athlete's Foot. Athletes' Foot causes dry, red, flaky skin around the feet and is transmitted usually in communal changing rooms and showers. To prevent it, we can wear appropriate footwear in these communal places. To treat it, we use anti-fungal medication.
Protists are eukaryotic organisms like fungal, Animal and Plant Cells. Protists are smaller than these other Eukaryotic Cells. As they are eukaryotic, protists store their genetic material in a nucleus. However, unlike other eukaryotic organisms, protists are often unicellular. They have characteristics very similar to plants, animals and fungi.
Protists are very interesting organisms; some are like animal cells, and others are much more similar to plant cells.
The main protist that you need to know is Plasmodium, which causes malaria. Malaria is spread by mosquitoes (vectors). This disease is found mainly in tropical areas. Malaria causes fever, sweats, headaches, vomiting and diarrhoea. The spread of malaria can be prevented by stopping individuals from being bitten. In order to prevent it, people can sleep under mosquito nets and wear long clothing, for example. If a person gets infected, they can be treated with antimalarial drugs.
Check out the Fungal Diseases and Protist Diseases articles to learn more about these types of diseases too
Communicable disease are diseases that can be spread from person to person.
Non-communicable diseases are diseases that cannot be spread from one person to another via pathogens.
Communicable disease are diseases that can be spread from person to person.
Pathogens such as viruses, bacteria, protists and fungi all can cause communicable diseases.
These diseases can be classified by the type of pathogens that cause them.
Flashcards in Communicable Diseases1811
Start learningWhat is a protist?
A group of eukaryotic, usually single-celled organisms of the kingdom Protista that are not plants, animals or fungi.
What is a Eukaryote?
An organism with cells that have a nucleus and other structures in the cytoplasm which have membranes around them.
What is a Vector?
An organism that does not cause disease itself but which spreads infection by conveying pathogens from one host to another
True or False: There is a vaccination for malaria.
True
What are the three types of protists?
Animal-like
Plant-like
Fungi like
How can plant protists be avoided?
Avoid dense planting to allow good air circulation around the plants
Pick off and dispose of affected leaves.
Remove and destroy severely affected plants.
Avoiding periods of high humidity in greenhouses by opening doors and vents to encourage air movement
Practice crop rotation.
Avoid watering plants in the evening.
Already have an account? Log in
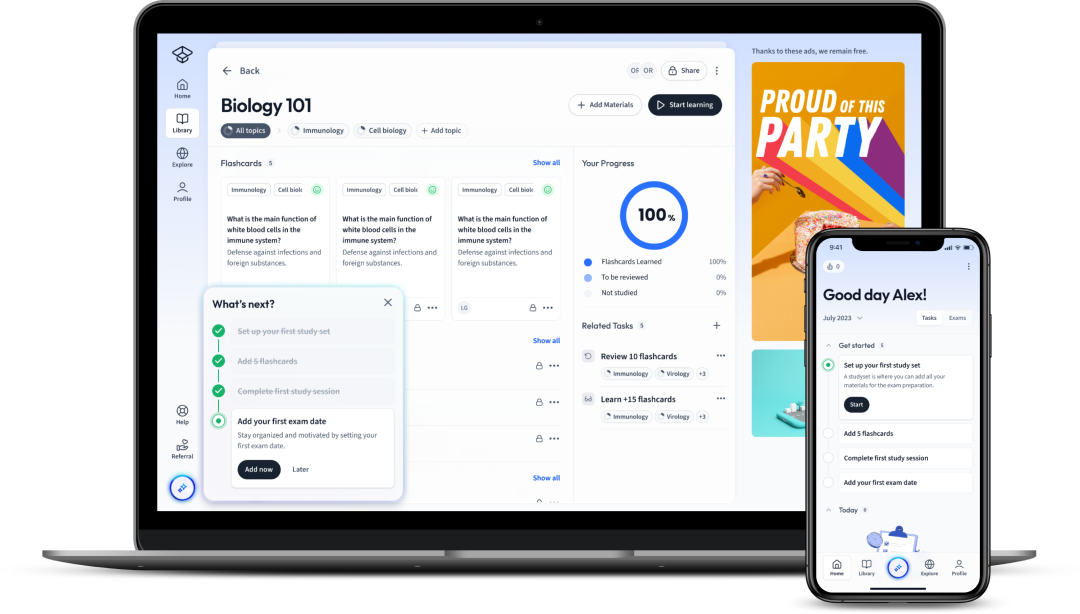
Open in AppThe first learning app that truly has everything you need to ace your exams in one place
Sign up to highlight and take notes. It’s 100% free.
Save explanations to your personalised space and access them anytime, anywhere!
Sign up with Email Sign up with AppleBy signing up, you agree to the Terms and Conditions and the Privacy Policy of StudySmarter.
Already have an account? Log in