
StudySmarter - The all-in-one study app.
4.8 • +11k Ratings
More than 3 Million Downloads
Free
Americas
Europe

Lerne mit deinen Freunden und bleibe auf dem richtigen Kurs mit deinen persönlichen Lernstatistiken
Jetzt kostenlos anmeldenPolitics includes activities associated with decision making, the role of states, conflict, and cooperation, and the distribution of resources, be it natural, human or other.
A central theme of politics is power, in fact, to study politics is to study power. Explaining who has power, who should have power and what power looks like is a foundational understanding of politics.
An insight made by Carol Hanisch, a political activist of second wave feminism, is that power exists at all levels of society, therefore, politics as a product of power, is more than the actions of prominent politicians seeking to exert influence over Governments. Politics permeates on all levels of society and is inclusive of the actions of everyday individuals.
 Signs stating ‘I care’, ‘I don’t’ and ‘I don’t know what’s happening’. Source: Tok2022
Signs stating ‘I care’, ‘I don’t’ and ‘I don’t know what’s happening’. Source: Tok2022
There are many angles to explore in the study of politics. However, throughout your learning process you will need to understand the origins and the constructions of political theory and political ideology.
Political theory helps us make sense of concepts that have shaped our politics and have formed the basis of political institutions. These concepts include freedom, justice, democracy and justice. Political theory seeks to evaluate, explain and predict political phenomena through the use of history, philosophy and science, and is therefore, based upon criticism.
Political theory provides the tools to which political ideologies are created.
Ideology means the science of ideas.
Political ideology is a huge component of political studies, you will encounter a number of political ideologies in your studies. It is important that you understand what ideologies are and what they seek to achieve. Political ideologies seek to establish 3 things :
A realistic interpretation of society
An idealised interpretation of society
How to create a society that reflects the needs and wants of all its citizens
Whilst political theory focuses on concepts such as freedom, ideologies take these concepts to establish an all-encompassing systematic doctrine. Ideologies attempt to present society with ideals that should be incorporated in its communities and a plan of how to achieve it. Unlike political theory, political ideology does not allow room for criticism.
Tip: When we refer to ideologies we normally think of a series of “isms” eg. conservatism, liberalism, feminism and anarchism
An example of the link between political theory and ideology is human nature.
Political theorists have investigated human nature to find objective truths on the nature of mankind. Many political theorists have forwarded the notion of human nature as being rational, and altruistic. Political ideology has used this view of human nature to serve as the foundation for ideologies such as anarchism. A key concept in anarchism is that as human nature is rational and altruistic there is no need for state rule, therefore, anarchism rejects all forms of state rule.
Tip: Think of political theory as a science experiment in which we are trying to prove a hypothesis, there is room to prove the hypothesis or disprove it. Political theory is rational, dispassionate and aims to establish objective truths on political matters.
UK politics features as one of the topics we will explore in order to develop your understanding of political systems. We will focus our learning on participation, democracy, political parties, elections and voting behaviour in the UK. We will provide you with an understanding of the current political system in the UK by delving into topics such as the suffrage movement. As a result, you will begin to understand the history of the political system(s) of the United Kingdom.
UK Politics |
|
It is important to understand the difference between UK politics and the UK Government, governance of the UK is political but not all politics is in relation to governance. When studying the UK Government we will move towards an understanding of where governance of the UK takes place, who governs the UK and how the UK is governed.
 The crest of the UK government. Source: Departement for Business, Enegry & Industrial Strategy
The crest of the UK government. Source: Departement for Business, Enegry & Industrial Strategy
This topic will equip you with a systematic insight into governance of the UK through an exploration of the Constitution. The Constitution establishes rules and laws that determine the roles and power of branches of Government. You will learn in-depth the structure and roles of Westminster Parliament, including the House of Lords and the House of Commons. This topic will equip you with the knowledge of the UK Government but will also give you a foundation for comparison when encountering the system of governance in other nations.
UK Government |
|
Ideologies are an important part of political study and you will be introduced to the traditional ideologies of liberalism, conservatism and socialism. Knowledge of these three ideologies is essential to political studies. You will learn these ideologies in-depth, this includes the key concepts of each ideology as well as notable thinkers from within each ideology. You will gain an understanding of how these ideologies interpret political theory through an exploration of the responses these ideologies have constructed in the matters of human nature, society and freedom.
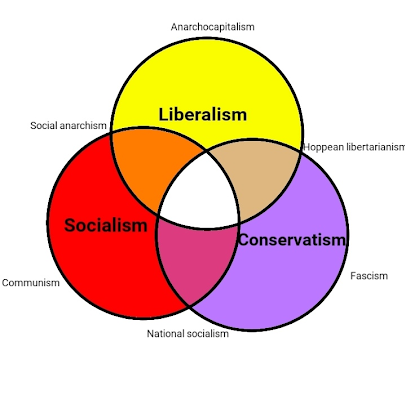 Venn diagram of liberalism, socialism and conservatism, Source: Google Pictures
Venn diagram of liberalism, socialism and conservatism, Source: Google Pictures
Core Ideologies |
|
After you’ve gained an established understanding of liberalism, conservatism and socialism you will be introduced to non-core ideologies. Depending on the syllabus for your school you will be introduced to one of the following - anarchism, nationalism, ecologism, multiculturalism or feminism. Similar to core ideologies, you will learn the key concepts of each of these ideologies. We will also explore and provide examples of the different types/variants we find in each ideology, to provide you with a well-rounded understanding of these 5 ideologies.
We refer to these ideologies as non-core ideologies because they emerge from or are influenced to some degree by the three core ideologies. Whilst you may be only required to learn one of the five ideologies for your syllabus we will introduce you to all five ideologies. Outside of your studies, it is useful to be familiar with these ideologies as they are heavily referenced in everyday life. An understanding of the debates within feminism, the different types of nationalism or the environmental concerns in ecologism will come in handy in the world beyond your syllabus.
Non-Core Ideologies |
|
The land of the free and the home of the brave. The USA positions itself as a global power and a beacon of democracy. How exactly is the United States governed? What is the nature of politics in the United States? These are questions that will be explored and answered in this topic. We will learn all about the governance of the US from its constitution to congress and the supreme court.

The United States is a global power, an understanding of US politics is critical as the Politics of this nation has had ramifications beyond its borders.You will cover all aspects of politics in the United States whilst delving into critical aspects of US politics such as the civil rights and race in the United states. You will also have the knowledge to start drawing comparative analysis between the US and the UK.
US Politics |
|
We live in an increasingly interconnected world. Distance does not stop our ability to message, Facetime or connect on social media with people from across the world. Similarly politics also has the ability to transcend borders. In global politics, we will cover the origins of the nation state and what national sovereignty means. We will also learn about an important phenomenon called globalisation. Globalisation is responsible for our increasing international connectivity. Furthermore, through an exploration into regionalism, we will analyse the politics of organisations such as the European Union, the African Union and the Arab league to gain an understanding of the many ways in which nationals have banded together to create multinational and international organisations. This topic gives you the opportunity to explore issues that affect people globally.

A globe made up of flags from many different nations, Source: STRAFASIA
Global Politics |
|
StudySmarter has all the topics, learning tools, quizzes, notes, and revision material you need to do well in your Politics course. Learn using our pre-made flashcards and revision guides. Alternatively, you can check out revision guides, quizzes, notes, and more that have been made by other students or even better, StudySmarter allows you to create your own with ease.
StudySmarter uses an intelligent learning plan that monitors your revision progress and motivates you to continue with revision and knowledge acquisition. StudySmarter will also help you to set weekly goals to keep track of your revision and achieve the best results possible. As you learn, you will earn badges for every achievement, motivating you to push forward.
If you like working with your friends, make sure to utilise our Study Groups. This tool allows you to share notes, flashcards and quizzes so that you can study together and share the workload.
StudySmarter is a free learning platform for students which allows them to create and share revision materials. Students can also select from a range of revision tools created by our subject experts from flashcards to extensive summaries.
The app offers an intelligent learning plan that tracks your child’s progress and keeps them motivated with badges and trophies.
Here are the advantages of using StudySmarter at a glance:
High-quality learning content
FREE summaries and exercises.
Collaborative study
A multitude of subjects to choose from
Flashcards in Politics7053
Start learningWhy do anarchists reject the state?
Anarchists reject the state as the state represents authority and has the ability to make someone do something they would have otherwise not have done.
Which of the following is an example of individualist anarchism?
Anarcho-capitalism.
Who is referred to as the founder of egoism?
Max Stirner.
What is liberal nationalism?
A form of nationalism that is exclusive.
Which time period did liberal nationalism emerge?
The French Revolution.
Which of the following is a form of liberal nationalism?
Civic nationalism.
Already have an account? Log in
Open in AppHow would you like to learn this content?
How would you like to learn this content?
Free politics cheat sheet!
Everything you need to know on . A perfect summary so you can easily remember everything.
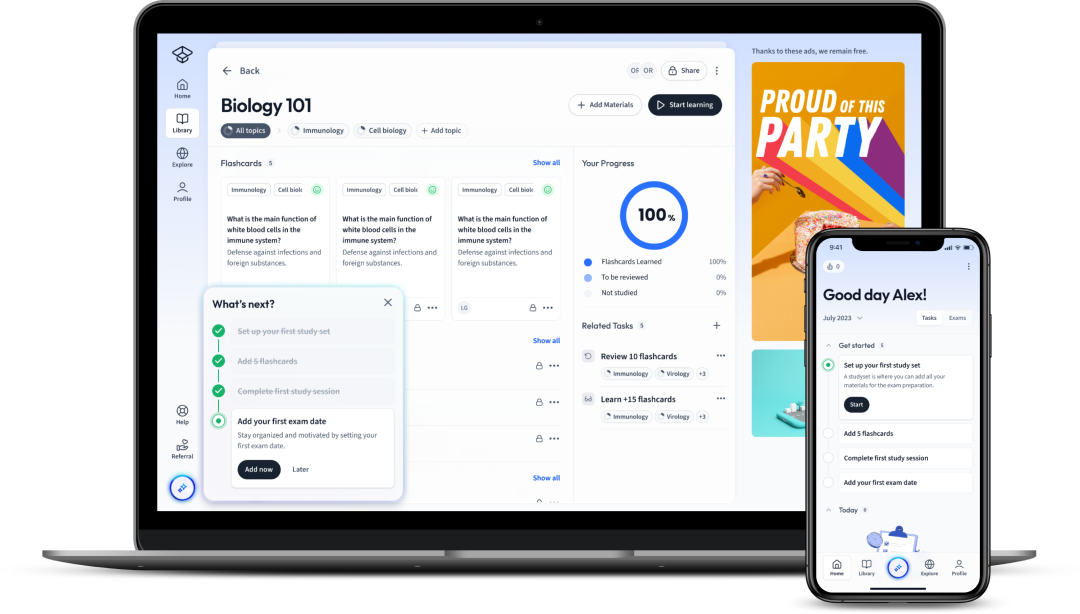
The first learning app that truly has everything you need to ace your exams in one place
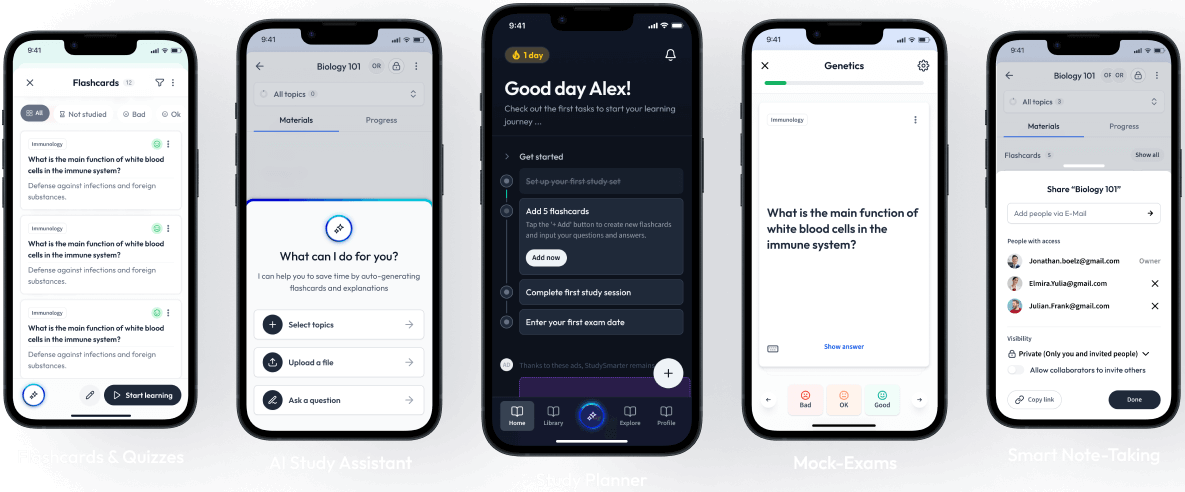
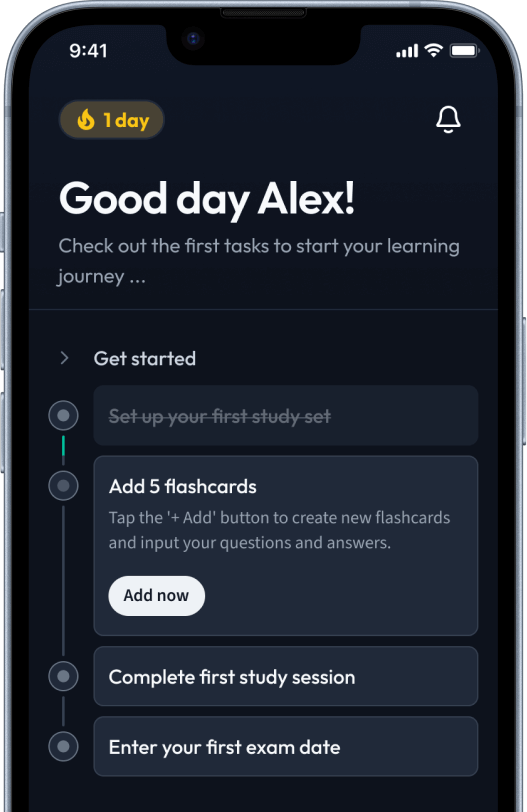
Sign up to highlight and take notes. It’s 100% free.
Save explanations to your personalised space and access them anytime, anywhere!
Sign up with Email Sign up with AppleBy signing up, you agree to the Terms and Conditions and the Privacy Policy of StudySmarter.
Already have an account? Log in